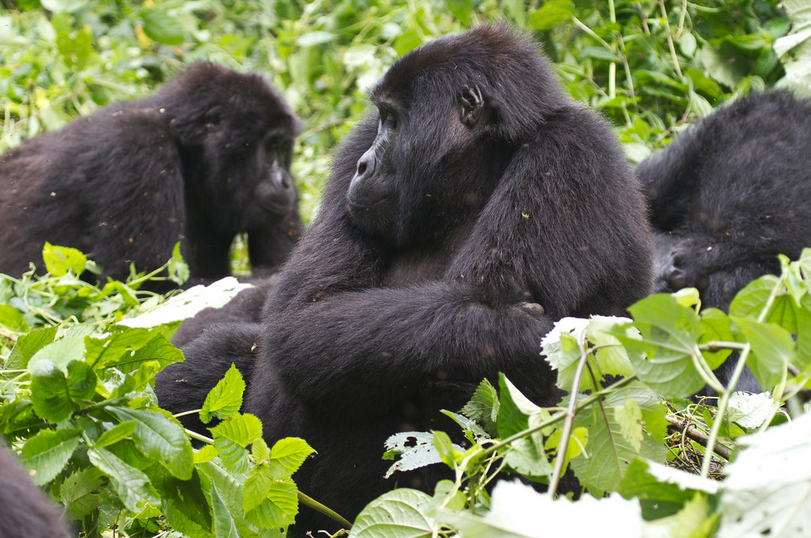
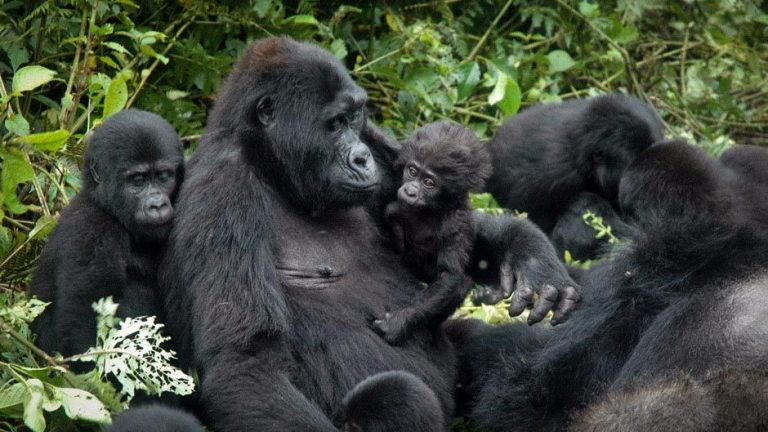
Mountain Gorillas : Generally, Uganda has two places where these mountain gorillas may be seen. These include; Mgahinga Gorilla, stunning park and component of the virunga and in Bwindi Impenetrable Forest National Park. However, the mountain gorilla (Gorilla beringei beringei) is one of the two subspecies of the eastern gorilla. Additionally, it is listed as critically endangered by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN).

Physical description
 Basically, the fur of the mountain gorilla is thicker and longer which enables them to live in colder temperatures. Firstly, the Adult males are called silverbacks because of a saddle of gray which develops on their backs with age.
Basically, the fur of the mountain gorilla is thicker and longer which enables them to live in colder temperatures. Firstly, the Adult males are called silverbacks because of a saddle of gray which develops on their backs with age.
Secondly, the hair on their backs is shorter than on most other body parts and their arm hair long. Gorillas can be identified by nose prints unique to each individual. Males have a weight of 195 kg and usually weigh twice as much as the females. Adult males have more pronounced bony crests on the top and back of their skulls, giving their heads a more conical shape.
Interestingly, the mountain gorilla is most active between 6:00 am and 6:00 pm. However, many of these hours are spent eating as large quantities of food are needed to sustain its massive bulk. It forages in early morning, rests around midday and in the afternoon it forages again before resting at night. Eventually, each gorilla builds a nest from surrounding vegetation to sleep in and constructing a new one every evening.
Gorillas leave their sleeping sites when the sun rises at around 6 am, except when it is cold they often stay longer in their nests. Like all great apes other than humans, its arms are longer than its legs. It moves by knuckle-walking, supporting its weight on the backs of its curved fingers rather than its palms.
Habitat and ecology
 The mountain gorilla generally inhabits the Albertine Rift montane cloud forests and of the Virunga volcanoes. The vegetation is very dense at the bottom of the mountains, becoming sparser at higher elevations. Besides, the forests where the mountain gorilla lives are often cloudy, misty and cold.
The mountain gorilla generally inhabits the Albertine Rift montane cloud forests and of the Virunga volcanoes. The vegetation is very dense at the bottom of the mountains, becoming sparser at higher elevations. Besides, the forests where the mountain gorilla lives are often cloudy, misty and cold.
The mountain gorilla spends most of its time in the Hagenia forests, where gallium vines are found year-round. It travels to the bamboo forests during the few months of the year when fresh shoots are available. The mountain gorilla is primarily herbivore; the majority of its diet is composed of the leaves, shoots and stems. It also feeds on roots (3.3%), flowers (2.3%), and fruit (1.7%), as well as small invertebrates (0.1%). Adult males can eat up to 34 kilograms of vegetation a day, while a female can eat as much as 18 kilograms.
Behavior
Social structure
 The mountain gorilla is highly social and lives in relatively stable, cohesive groups held together by long-term bonds. The dominant silverback generally determines the movements of the group, leading it to appropriate feeding sites throughout the year. He also mediates conflicts within the group and protects it from external threats.
The mountain gorilla is highly social and lives in relatively stable, cohesive groups held together by long-term bonds. The dominant silverback generally determines the movements of the group, leading it to appropriate feeding sites throughout the year. He also mediates conflicts within the group and protects it from external threats.
When the group is attacked by humans, leopards, or other gorillas, the silverback will protect them. Besides, he is the center of attention during rest sessions and young gorillas frequently stay close to him. If a mother dies or leaves the group, the silverback is usually the one who looks after her abandoned offspring. Nevertheless, the silverback dies or is killed by disease, accident, or poachers, the family group may be disrupted. In addition, when a new silverback joins the family group, he may kill the infants of the dead silverback.
A typical group contains: one dominant silverback, who is the group’s undisputed leader. Another subordinate silverback (usually a younger brother, half-brother, or even an adult son of the dominant silverback). One or two black backs who act as sentries. Three to four sexually mature females who are ordinarily bonded to the dominant silverback for life and from three to six juveniles and infants.
Males leave when they are about 11 years old and often the separation process is slow. On the other hand, they spend more and more time on the edge of the group until they leave altogether. They may travel alone or with an all-male group for 2–5 years before they can attract females to join them. Females typically emigrate when they are about 8 years old. In summary, females often transfer to a new group several times before they settle down with a certain silverback male.
Affiliation
The midday rest period basically is an important time for establishing and reinforcing relationships within the group. In addition, mutual grooming reinforces social bonds and helps keep hair free from dirt and parasites. Young gorillas play often and this helps them learn how to communicate and behave within the group. Activities include wrestling, chasing, and somersaults. However, the silverback and his females tolerate and even participate if encouraged.
Fears
For reasons unknown, mountain gorillas that have been studied appear to be naturally afraid of certain reptiles and insects. They are also afraid of water and will cross streams only if they can do so without getting wet.
Vocalization
Sounds classified as grunts and barks are heard most frequently while traveling and indicate the whereabouts of individual group members. They may also be used during social interactions when discipline is required. On the other hand, screams and roars are used for alarm or warning and are produced most often by silverbacks.
Aggression

Although strong and powerful, the mountain gorillas are generally gentle and very shy. Severe aggression is rare in stable groups but when two groups meet, the two silverbacks can sometimes engage in a fight to death. Therefore, conflicts are most often resolved by displays and other threat behaviors that are intended to intimidate without becoming physical.
Habitat loss
This is one of the most severe threats to gorilla populations. The forests where mountain gorillas live are surrounded by rapidly increasing human settlement. Through shifting (slash-and-burn) agriculture, pastoral expansion and logging, villages in forest zones cause fragmentation and degradation of habitat. Furthermore, the impact of habitat loss extends beyond the reduction of suitable living space for gorillas.
Poaching
Mountain gorillas are not usually hunted for bush meat but they are frequently killed by traps and snares intended for other animals. They have also been killed for their heads, hands, and feet, which are sold to collectors. Infants are sold to zoos, researchers, and people who want them as pets. The abduction of infants generally involves the loss of at least one adult, as members of a group will fight to the death to protect their young
Disease
The mountain gorilla is also at risk from people of a more well-meaning nature. Groups subjected to regular visits from tourists and locals are at a continued risk of disease cross-transmission. This led to attempts to enforce a rule that humans and gorillas be separated by a distance of 7 metres at all times to prevent this. With a similar genetic makeup to humans and an immune system that has not evolved to cope with human disease, this poses a serious conservation threat.
Why Bwindi Impenetrable National Park?

This park is among the most visited national parks in the country. It is also popularly known as home of mountain gorillas which are among the endangered species in the world today. Records show that thousands and thousands of tourists travel from all the parts of the world specifically to come and see these internationally endangered gorillas during the Uganda Gorilla Trekking Tours. Besides these, there is a great diversity of other wildlife including small wild animals, primates.
Bwindi Impenetrable National Park is located in south western Uganda and is divided into four regions. These include; Buhoma in the North, Ruhija in the East, Rushaga and Nkuringo in the south. Meanwhile, each region has been given habituated gorilla families for gorilla trekking. If you are to trek gorillas in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park. For more details, contact Great Nest Image Safaris about Bwindi Gorilla treks and holidays.
How close are gorillas related to man?
Gorilla’s hands and feet resemble the human ones more than those of other Apes. Gorillas spend more time on the ground than other Apes; hence their feet are more suited of walking. The genetic material of Apes is identical to that of humans to a very large degree. Difference are especially small in nuclear DNA.1.2% between humans and chimpanzees, 1.6% between humans and gorillas.
How often do mountain gorillas give birth?
Female gorillas are sexually mature at around 7 to 8 years of age; however, they don’t usually reproduce until they are 10 years old. Males mature later than females and are rarely strong and dominate enough to reproduce before 15 to 20 years of age.
How big are the giant apes?
 Gorillas are the largest species of primates and the males are often twice as big as the females. The males grow to around five and a half (5.5) feet tall and weigh around 400 pounds whereas females grow to (4.5) feet tall and around 200 pounds.
Gorillas are the largest species of primates and the males are often twice as big as the females. The males grow to around five and a half (5.5) feet tall and weigh around 400 pounds whereas females grow to (4.5) feet tall and around 200 pounds.
Generally, gorillas have long arms, even longer than their legs and they use their long arms to walk. This is where they use the knuckles on their hands to walk on all fours. Gorillas from different areas may have different colored hair. Like the western gorilla has the darkest and the western low land gorilla can also have the greyish color and red colored forehead. All in all, when the male gorillas get old, their hair turns white on their back and those are called Silverbacks.
Fun facts about gorillas
- Gorillas have hands and feet like humans including opposable thumbs and big toes.
- Interestingly, some gorillas in captivity have learned to use sign language to communicate with humans.
- Gorillas live in small groups called troops or bands.
- Gorillas live around 35years.
- They sleep in nests.
What do they eat?
Gorillas are herbivores and they feed on plants i.e. leaves, steam pith, fruits and bamboo.
What is gorilla trekking?
Gorilla trekking is an activity where tourists/people go searching for gorillas in the wild. Additionally, Gorilla trekking is currently available in three African countries; Uganda, Rwanda and Democratic Republic Of Congo. The process of gorilla trekking normally starts with an early morning briefing at the respective park headquarters. Then a hike or walk into the forest following the trail used by Mountain gorillas and once found, you spend only one hour with them. You will then return back and be offered a certificate. The trek its self may take up to 30 minutes or three quarters of the day but once you find gorillas, you are allowed to spend one hour with them.
What is the age limit for gorilla trekking?
Age limit for gorilla trekking in Uganda and Rwanda is 15 years and above. The authorities are very strict on this, so kindly make sure all clients and children are 15 or older in order to avoid any sad incidents like guest(s) kids being refused to track!
How many people per gorilla family?
Only a maximum of 8 people are allowed to trek or visit a given gorilla family in Bwindi, Mgahinga and Volcanoes national parks. Bwindi has about 14 habituated gorilla families and thus each family is allowed only 8 people per day per hour. On the other hand, when it comes to gorilla habituation, its only 4 people that are allowed to spend 4 hours with Mountain gorillas under habituation.
What are the chances of seeing mountain gorillas?
 We gladly confirm that chances of seeing gorillas either in Bwindi National Park or volcanoes is 98%. Besides, gorilla trekking in Bwindi, Mgahinga and Volcanoes in Rwanda is so organized in a way that there is an advanced team of trackers who wake up every morning to find where these gorillas are.
We gladly confirm that chances of seeing gorillas either in Bwindi National Park or volcanoes is 98%. Besides, gorilla trekking in Bwindi, Mgahinga and Volcanoes in Rwanda is so organized in a way that there is an advanced team of trackers who wake up every morning to find where these gorillas are.
Once they find them, they will then communicate to the park headquarters and your ranger guide of the day will let you know of the whereabouts of these gorillas. You will then start your trek from where the gorillas would have slept the previous night up to when you find them. Meanwhile, the advanced team will keep communicating with your guide to make sure you don’t get lost. If the gorilla family keeps moving very fast, communication will be made.
What should I pack for gorilla trekking?
Gorilla trekking clothes are the same for Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, Mgahinga National Park as well as Volcanoes National Park. You need to prepare very well for your gorilla trek therefore, we advise the following. Trousers, long sleeved shirts or blouses, long socks to enable you tack in your trousers, garden gloves, a hat, sun glasses, hiking boots, rain jacket, cameras and extra batteries, insect repellents and some energy giving foods.
When is the best time to trek gorillas?
Mountain gorillas in Uganda and Rwanda can be trekked throughout the whole year but most especially done in the drier months. Uganda being crossed by the Equator has a modified equatorial climate with two rainy seasons. Because of this, people tend to associate these rainy seasons with the best times to trek gorillas. When it is raining, it becomes hard to hike and trek in the impenetrable forest because of the heavy rains which makes the trails too slippery. Besides that, vegetation tends to grow something that reduces chances of proper visibility and photography.
In other words, the best time is in June, July, August, early September and part of October then December up to February. However, because of global warming it is even becoming very hard to predict when it is going to rain or not. During high season gorilla permits to visit gorillas in Rwanda’s Volcanoes National Park and Bwindi National Park is at $1500.00 and $700.00 per person respectively.
What is the price of a gorilla tour in Uganda?
When looking at the price of a gorilla tour in Uganda, you need to consider the three main components. These include; gorilla permit, accommodation and transport to and from the park. A gorilla permit price in Uganda currently costs $700. Accommodation rates range from $50 for Budget up to $500 and more for luxury lodges per person sharing. On the other hand, you might choose to drive or fly to Bwindi Impenetrable National Park.
When do I need to book a gorilla permit?
Gorilla permits tend to sell out quickly so it is always advised to book your gorilla permit in advance. At Great Nest Image Safaris, we advise that you book your gorilla permit in 3-4 months in advance to avoid short notice disappointments. Gorilla permits tend to run out during the high seasons of June, July, August, September, December, January and February each year. Please contact Great Nest Image Safaris for details about availability and cost of securing gorilla permits.
How much is a gorilla permit in Uganda or Rwanda?
 Gorilla tracking takes place in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park and Mgahinga National Park and one requires permission in order to watch or view mountain gorillas. This therefore means that you will purchase a gorilla permit to allow you see mountain gorillas in Uganda or Rwanda. A gorilla permit is an electronic document/card that is obtained from Uganda Wildlife Authority head office in Kampala and it is this card that you will take to Bwindi Impenetrable National Park headquarters on the day of gorilla trekking. Once it is checked and found valid, you will then be allowed to trek gorillas.
Gorilla tracking takes place in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park and Mgahinga National Park and one requires permission in order to watch or view mountain gorillas. This therefore means that you will purchase a gorilla permit to allow you see mountain gorillas in Uganda or Rwanda. A gorilla permit is an electronic document/card that is obtained from Uganda Wildlife Authority head office in Kampala and it is this card that you will take to Bwindi Impenetrable National Park headquarters on the day of gorilla trekking. Once it is checked and found valid, you will then be allowed to trek gorillas.
Therefore, in Rwanda a gorilla permit costs $1500.00 (Non-residents) and Uganda gorilla permits to visit mountain gorillas in Bwindi National Park and Mgahinga costs $700.00 per permit. Foreign residents with a valid working permit pay $500.00 and East African citizens of Uganda, Rwanda, Kenya, Burundi and Tanzania pay Uganda shillings 250,000 only.
When should I book my gorilla permit?
You are advised to book your gorilla permit at least three months in advance especially during high season. Please contact us with the date when you intend to trek and we will advise availability of permits on that day.
How should I book a gorilla permit?
Uganda Wildlife Authority is the body mandated to sell or issue out gorilla permits. This is because they are the ones in charge of all National Parks in Uganda including Bwindi Impenetrable National Park and Mgahinga National Park. Before you book a gorilla permit, you have to first identify the year, month and date when you intend to trek gorillas in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park. Once you have that in mind, then contact us and we will check availability for you and we will let you know if the date you are interested in is possible. Booking a gorilla permit must be done with cash and thereafter, we will invoice you for full payments. Additionally, you will have to provide us with your passport details as they are required by Uganda Wildlife Authority for two reasons;
- Firstly, Uganda Wildlife Authority would like to know if indeed you are eligible or have the right age allowed to trek mountain gorillas. Age limit for gorilla trekking in Uganda and Rwanda is 15 years and above.
- Secondly, it is to establish if you are a foreign resident or none resident or even East African since this will affect the price of a gorilla permit.
Due to the fact that we book gorilla permits in the absence of our client who mostly book in advance, we have to scan and send them a copy. However, the original copies are handed to you at your arrival at the airport since they will be required on the very trekking day. We do not charge anything for booking a gorilla permit if client books an all-inclusive tour with us.
What is included in a gorilla permit?
A gorilla permit allows you one hour with mountain gorillas in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, Mgahinga or Volcanoes National Park. Included in the cost are park entry fees for the respective parks, services of National Park guides/rangers whop will escort you to the forest.
How long is gorilla trekking in Uganda or Rwanda?
Mountain gorilla trekking exercise can take from twenty minutes to three quarters of the day so one needs to prepare for both. This depends on several factors that include;
- Mountain gorilla movements, where the gorillas stayed the previous night and the mood of the gorillas.
- It may also depend on the people in your group since the guides/rangers move following the slowest person in the group.
Is it possible to trek Uganda gorillas via Kigali?
It is now possible to trek Uganda or Bwindi gorillas through Rwanda by flying through Kigali International Airport. By flying through Kigali International Airport, one is able to reduce the drive time to Bwindi Impenetrable National Park to 5-6 hours compared to if one uses Entebbe International Airport. With the introduction of the East African tourist visa, one can now visit both Uganda and Rwanda. East African tourist visa costs USD 100.00 and allows you to visit three East African countries of Uganda, Rwanda and Kenya. Please contact Great Nest Image Safaris for details about Bwindi gorilla safaris through Kigali Airport.
What is gorilla habituation experience?
 Gorilla habituation experience is an activity in Bwindi Impenetrable national park where tourists are allowed to stay four hours with mountain gorillas.
Gorilla habituation experience is an activity in Bwindi Impenetrable national park where tourists are allowed to stay four hours with mountain gorillas.
Tourists are able to see gorillas while participating in activities geared to making these wild mountain gorillas get used to human beings. Gorilla habituation safaris are currently taking place only in Rushaga located in south. However, only four people are allowed to see these gorillas in Bwindi National Park and we do organize gorilla habituation experience safaris at affordable prices.
Do you have any questions about gorillas?
Please send us an email and we will answer all your questions concerning gorilla trekking to enable you prepare a memorable experience with us.
Gorilla permit costs
Gorilla trekking permit costs 700USD per person and you get to spend only one hour with the mountain gorillas while Gorilla Habituation costs 1500USD per person. This also allows you to spend four hours with the mountain gorillas. However, gorilla trekking permit is inclusive of the park entry fee and should be paid in advance through Uganda Wildlife Authority Offices or through our Company.
Requirements for the safari
- Gorilla trekking permits.
- Proof of Yellow fever vaccination.
- Good physical, fit health and mental condition.
- Uganda Visa which can be got on arrival at the Airport.
- Travelers must be at least 15 years old on the day the trekking.
- Travel & Health insurance arranged from your home Country.
- Hiking shoes.
- Water proof Jacket.
- Long Sleeves shirt & Waterproof Pants.
- Warm Jacket.
Request a Quote
Featured Tour Updates
Permit cost for gorilla trekking in Uganda
Permit cost for gorilla trekking in Uganda Permit cost for gorilla trekking in Uganda : Gorilla trekking is one...
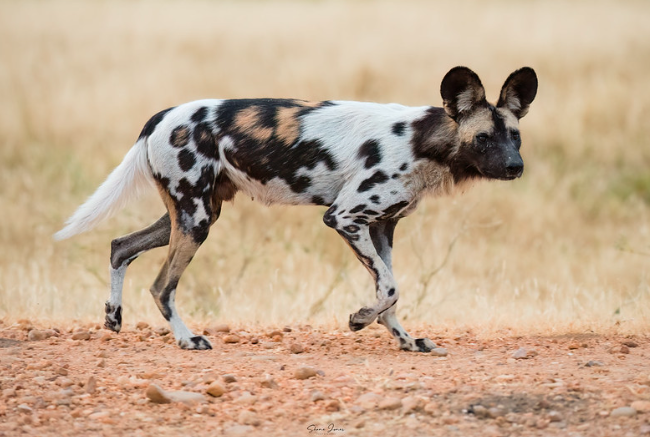
The African Wild Dog
The African Wild Dog The African wild dog: (Lycaon pictus) also known as the African painted dog or Cape...
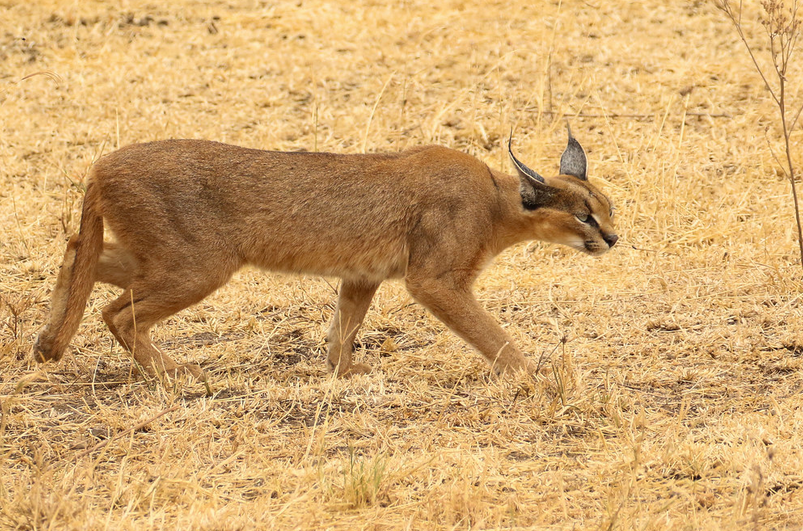
The Caracal (Felis caracal)
The Caracal (Felis caracal) The Caracal (Felis caracal): is a medium-sized wild cat that can run up to 50...
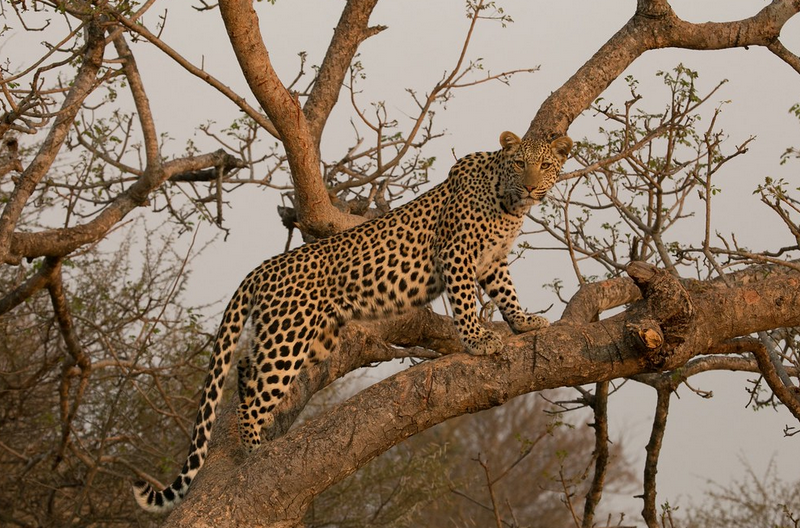
African Leopards (Panthera pardus)
African Leopards (Panthera pardus) African Leopards (Panthera pardus) : are one of the most feared but respected animals in...